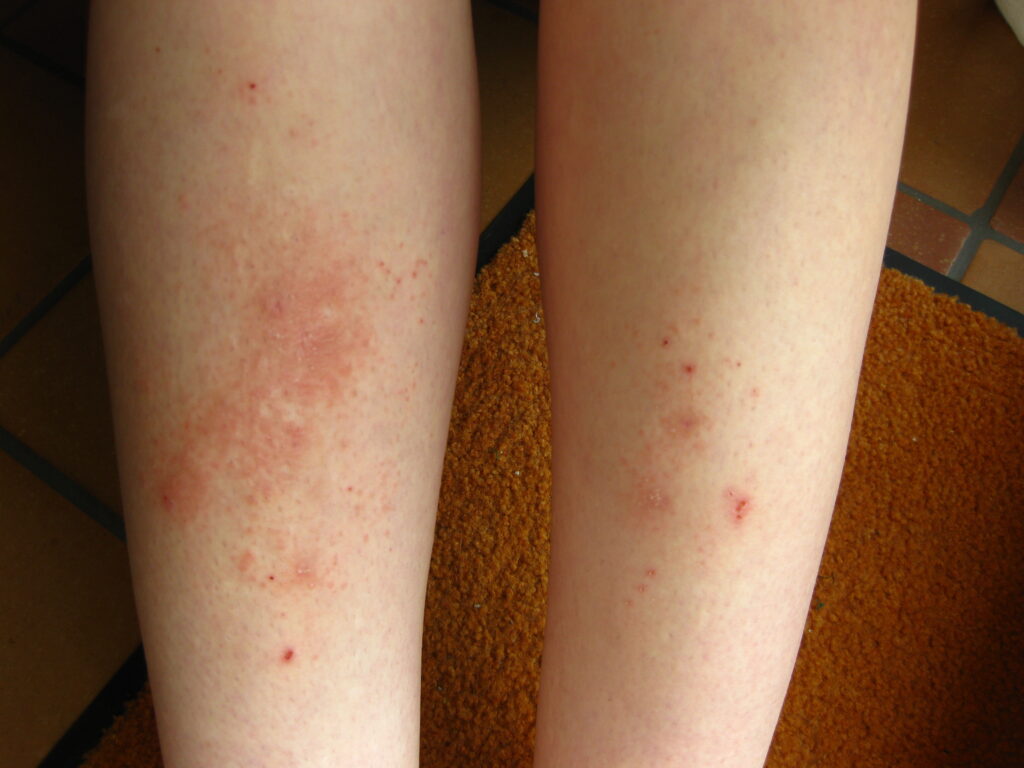
Also known as neurodermatitis or scratch dermatitis, this condition is caused by a chronic cycle of scratching and itching an area of skin that becomes rough or leathery. While it is not dangerous, Lichen Simplex Chronicus can be a difficult cycle to break because of the severity of the itchiness. It can occur anywhere on the skin but is most commonly found on the ankles, neck, wrist, forearms, thighs, lower leg, behind the knee, or on the inner elbow. It may also be associated with other skin conditions, such as dry skin, eczema, or psoriasis.
Lichen Simplex Chronicus occurs more frequently among women than men and generally appears in people between the ages of 30 and 50. If you are unable to break a scratch and itch cycle somewhere on your skin or if the skin becomes painful, contact your dermatologist. Persistent scratching can lead to bacterial infection. The doctor may prescribe oral corticosteroids and antihistamines to reduce the inflammation and relieve the itching. In some cases, antidepressant or anti-anxiety medications provide relief to sufferers. If scratching does lead to an infection, your dermatologist will likely prescribe an oral or topical antibiotic.
Some patients gain relief from the itching by applying a moisturizing lotion and covering the area with a wet dressing. Moisture helps the skin absorb the lotion. Peeling ointments containing salicylic acid may also be recommended to soften rough skin.